Sargassum monitoring has just released the following statements regarding,, k…
Sargassum Monitoring Has Just Released the Following Statements Regarding Recent Developments
In recent months, Sargassum monitoring efforts have gained significant attention due to the increasing prevalence and impact of this seaweed on coastal environments worldwide. The latest statements released by Sargassum monitoring agencies highlight both the challenges posed by the surge in sargassum blooms and the innovative strategies being employed to address them.
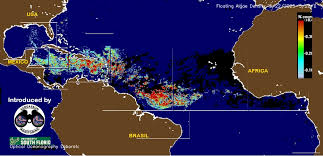
Sargassum, a type of large brown seaweed, naturally occurs in the Atlantic Ocean, particularly in the Sargasso Sea. However, over the past decade, there has been a notable increase in its abundance, leading to massive seaweed influxes along the Caribbean, Gulf of Mexico, West Africa, and parts of the Atlantic coasts. These blooms can stretch for hundreds of miles and have a profound impact on marine ecosystems, tourism, fishing industries, and local communities.
The agencies responsible for monitoring sargassum, including NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration), regional environmental bodies, and research institutions, have emphasized the importance of accurate and timely data collection. Their recent statements underscore advancements in satellite technology, drone surveillance, and in-situ measurements that have enhanced the ability to track sargassum distribution, density, and movement patterns.
One key point highlighted is the development of predictive models that utilize satellite imagery and oceanographic data to forecast sargassum blooms weeks in advance. These models are crucial for coastal communities and industries to prepare and implement mitigation strategies. For example, early warnings enable shoreline clean-up operations, inform tourism advisories, and help fisheries manage their activities to minimize economic losses.
Furthermore, the statements address ongoing research into sustainable and environmentally friendly methods of managing sargassum accumulation. Traditional approaches, such as mechanical removal and burning, often pose environmental concerns and logistical challenges. Recent initiatives focus on exploring alternative uses for sargassum, including conversion into biofuel, fertilizer, animal feed, and even building materials. These innovative solutions aim to turn a problematic phenomenon into an economic opportunity while reducing ecological harm.
The agencies also acknowledge the need for international collaboration, given that sargassum blooms are a transboundary issue affecting multiple nations. They advocate for shared data platforms, joint research projects, and coordinated response strategies to effectively address the growing challenge. In addition, they stress the importance of community engagement, urging local populations to participate in monitoring efforts and adopt sustainable practices.
Climate change is frequently mentioned as a contributing factor to the increasing frequency and intensity of sargassum blooms. Rising sea temperatures, changing ocean currents, and nutrient runoffs from agriculture and urban development create ideal conditions for sargassum proliferation. The current statements call for integrated approaches that consider these environmental drivers and promote policies aimed at reducing nutrient pollution and preserving marine health.
In conclusion, the recent statements from sargassum monitoring agencies reflect a proactive stance in managing this complex issue. Emphasizing technological advancements, sustainable management practices, and international cooperation, these organizations aim to mitigate the adverse effects of sargassum blooms and explore opportunities for turning a challenge into a benefit. As climate change continues to influence ocean dynamics, ongoing research and adaptive strategies will be vital in safeguarding coastal ecosystems and supporting the communities that depend on them.
Leave a Reply